[responsivevoice_button rate=”1″ pitch=”1.2″ volume=”0.8″ voice=”US English Female” buttontext=”Story in Audio”]
How to overclock your PC’s CPU
If you think that overclocking is solely for performance-obsessed geeks armed with bottles of liquid nitrogen, it’s time to reconsider! Even a small bump in PC performance can delay the need to upgrade your CPU, keeping money in your pocket.
Today I’ll walk you through simple overclocking steps that can boost processor speeds 10 percent or more. If you’re a gamer, video artist, or media streamer, that’s a useful, no-cost upgrade. Read on if you want your PC to go faster!
What is overclocking, anyway?
Overclocking is a technique for tweaking various types of PC hardware, so that it runs faster than the manufacturer’s intended specification. Many processors, RAM modules, and graphics cards can be overclocked, usually by adjusting their settings via your motherboard’s UEFI BIOS. Operate in safe margins and overclocking shouldn’t damage your PC. But, as we’ll discuss, it’s important to manage the additional heat that accelerated hardware can generate.
Some tips for the journey
There are a few guiding principles worth considering before you overclock a CPU. First, not all processors can be easily overclocked. If you’re Team AMD, you’re probably in luck, as all modern Ryzen processors can be overclocked in B- and X-series AM4 motherboards. Intel, however, locks most of its mainstream CPUs to prevent smart users from purchasing a budget component and jacking up its performance. Pricier enthusiast processor lines (identified by a K or X suffix, such as the Intel Core i5-10600K), on the other hand, are sold unlocked and can therefore be overclocked.
Even then, bear in mind that processors are unique slabs of silicon and electronics. Some processors can tolerate higher operating speeds better than others—even those of the same model and specification. It’s known as the “silicon lottery” for a reason!
Stable overclocks entail a delicate balance of speed and heat. The more you push your processor, the hotter it’s going to get. If your PC becomes a little too toasty, integrated fail-safe measures should shut off the power before those expensive components are damaged. To keep your overclocked PC stable, your job is to keep it cool.
Budget CPU coolers (the stock heatsink-and-fan assembly that ships with many processors) are going to struggle here. Consider upgrading to a better-performing air cooler (such as those from Noctua) or investigate all-in-one liquid coolers, which work much like a car’s radiator. I recently upgraded my gaming rig with the NZXT Kraken X62 which pumps coolant over the CPU via a sealed system, then extracts the heat via a large radiator and double-fan assembly, mounted in the top of the case.
 NZXT
NZXTNZXT Kraken X62
We’re about to get hands-on with a motherboard’s UEFI BIOS software, which allows fine-tuning of your hardware settings. However, some motherboard manufacturers offer convenient apps that attempt to safely overclock your CPU for you. If these manual steps seem a little tough, then check out the likes of Asus Dual Intelligent Processors 5, Gigabyte EasyTune, AMD’s Ryzen Master, or Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility. MSI motherboards even have a physical OC Genie button you can press to turbocharge your PC.
Overclocking basics
For this guide, I’m using an Asus Maximus VIII Hero Alpha motherboard with an Intel Core i7-6700K processor. Obviously, these steps may need to be tweaked for your particular hardware, but the principles still apply.
Before you get started, be sure to download and install the latest BIOS software for your motherboard from the manufacturer’s website. It’s an important step to ensure you have the latest configuration options and that your efforts aren’t frustrated by known issues.
Let’s boot up the PC, press F2 (or Delete) at startup to access the BIOS, and get started.
As you can see below, this processor runs at a base frequency of 4GHz (4,000MHz). It’s also equipped with a Max Turbo feature that boosts speeds to 4.2GHz when required. When idle, the CPU temperature is a cool 25 degrees C, with a core voltage of 1.264V—the amount of power that’s being supplied to the CPU.
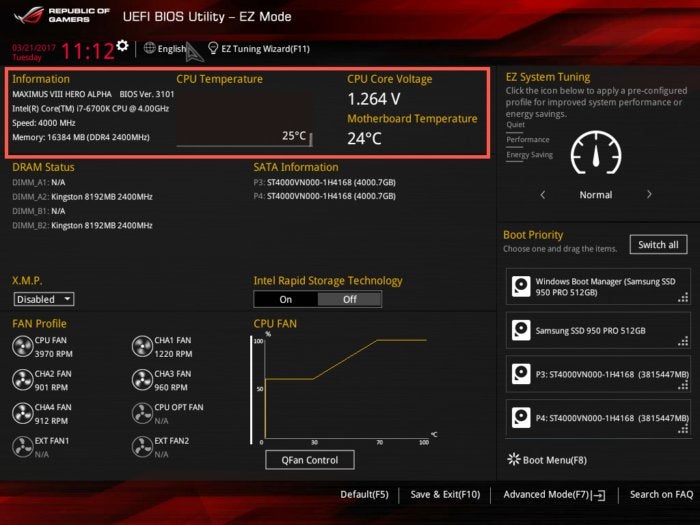 Terry Walsh/IDG
Terry Walsh/IDGClick F7 to switch to Advanced Mode, which is where we’ll be spending most of our time in this guide (see below). On the right of the screen, there are two additional settings to mention: BCLK is the base clock frequency, currently set to 100MHz. Underneath that, you’ll see a Ratio setting (often known as the multiplier). Your processor speed is a simple calculation of the base clock speed multiplied by the ratio. In this example, 100MHz x 40 equals 4,000MHz (4GHz).
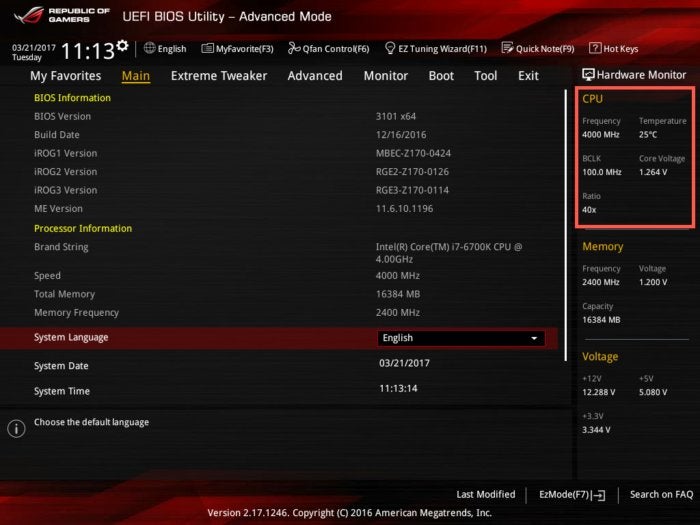 Terry Walsh/IDG
Terry Walsh/IDGTo overclock the CPU, we can adjust the base clock frequency or the ratio/multiplier to achieve a faster CPU frequency. A ratio of 42x with the same 100MHz base clock speed would deliver a CPU frequency of 4,200MHz, or 4.2GHz.
Switching to manual control
Modern motherboards can be equipped with a raft of automated settings designed to make overclocking easy.
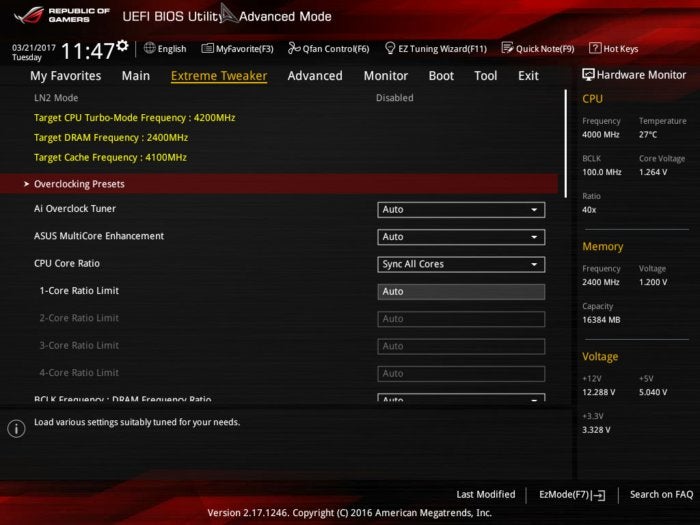 Terry Walsh/IDG
Terry Walsh/IDGIn the Asus Extreme Tweaker menu, we switch the Ai Overclock Tuner from Auto to Manual, which allows access to the base clock frequency setting. You can now type a value into the BCLK Frequency field. Hold fire for now, though.
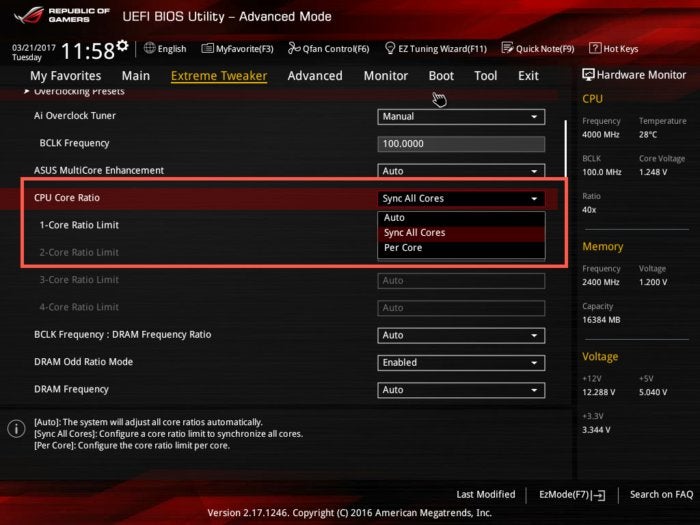
Below, you’ll see CPU Core Ratio, which allows us to adjust the multiplier. Some motherboards allow you to target individual processor cores or apply one setting across all cores. Why? Applying the same ambitious overclocking profile to all processor cores may make your PC unstable. But, dial back the settings on individual cores and you may achieve a better balance.
 Terry Walsh/IDG
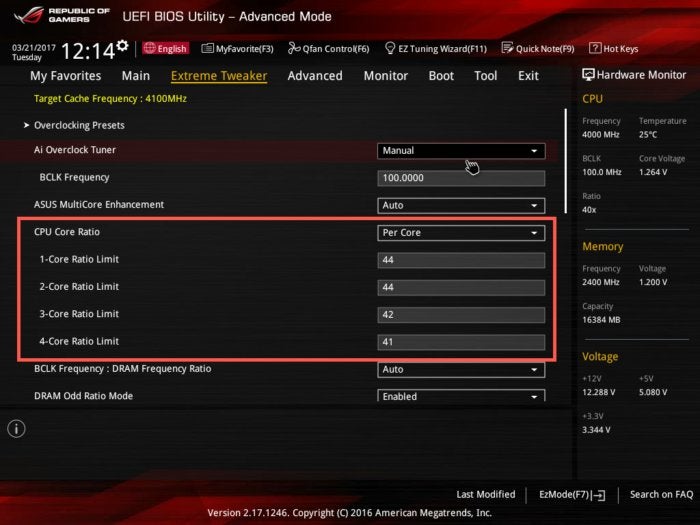
Terry Walsh/IDGWith the CPU Core Ratio set to anything other than Auto, the Core Ratio Limit settings become editable. Sync All Cores enables the 1-Core Ratio Limit setting. Any value you type here is applied across all four cores. Select Per Core and you can target each core individually.
 Terry Walsh/IDG
Terry Walsh/IDGWe’ll synchronize speeds across all cores in this guide, but feel free to play with individual core settings if required.
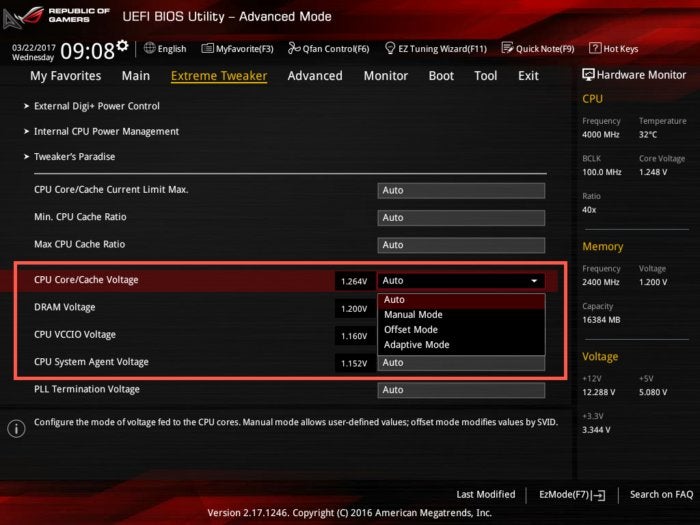
Before we make any changes to the base clock frequency or CPU ratios, there’s an additional element to consider: voltage. The voltage applied to your CPU varies continually. Faster operating speeds require additional power for stability. Your motherboard handles this behind the scenes but, should you wish, you can set manual voltage levels to support your overclocking efforts.
 Terry Walsh/IDG
Terry Walsh/IDGScroll down to CPU Core/Cache Voltage and click the drop-down menu. You can see three alternative settings. Manual Mode sets a single, static voltage level. Whether your CPU is idle or running at full tilt, the same voltage will be applied. Thinking about power consumption, Manual Mode is quite inefficient, but gives you the most control.
Offset Mode works by adding (or subtracting, if you wished to underclock) a set amount of power to the standard voltage that the processor would use. The voltage would still vary based on requirements, but the range would be boosted by whatever step you configured. So, if you created an offset of 0.1 V, for example, and the processor typically requires 1.25 V to deliver a certain speed, 1.35 V would actually be supplied.
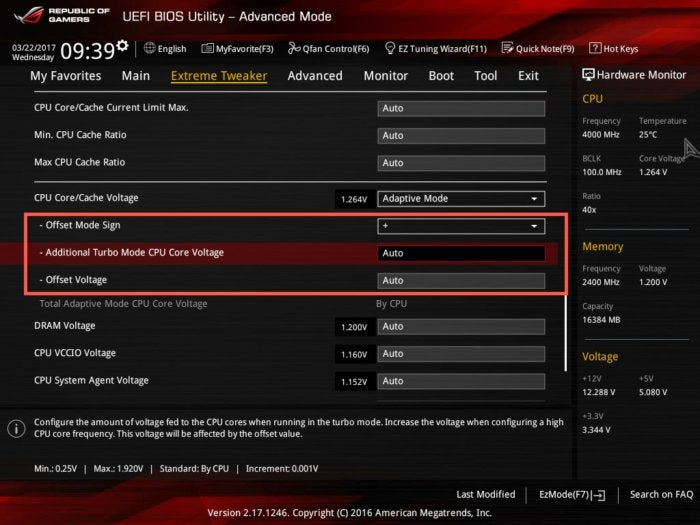
In Adaptive Mode, your CPU would only receive a voltage boost when it enters turbo mode. It’s worth noting that, on some motherboards, you can also include an Offset value for Adaptive Mode, that also provides a voltage boost to the processor outside of turbo mode.
 Terry Walsh/IDG
Terry Walsh/IDGIf you’re taking your first steps in overclocking, allow your motherboard to handle voltage automatically—at least until you’ve built up some experience. If you experience instability, then experiment with Adaptive and Offset modes to support your CPU with a small voltage boost. Benchmarking PCs in manual voltage modes can place significant stress on the CPU, increasing their risk of failure.
Be sure to also pay attention to any contextual help provided in your UEFI BIOS, or motherboard manual. In the screenshot above, you can see guidelines at the bottom of the screen outlining minimum and maximum voltage settings, as well as the increment to use.
Next page: Walkthrough and benchmarking